
What is the partial pressure of each gas at 20.00☌, and what is the total pressure in the cylinder at this temperature? A typical gas cylinder used for such depths contains 51.2 g of O 2 and 326.4 g of He and has a volume of 10.0 L. We can write it mathematically asįor reasons that we will examine in Chapter 13 "Solutions", deep-sea divers must use special gas mixtures in their tanks, rather than compressed air, to avoid serious problems, most notably a condition called “the bends.” At depths of about 350 ft, divers are subject to a pressure of approximately 10 atm. It is now known as Dalton’s law of partial pressures A law that states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of component gases. This law was first discovered by John Dalton, the father of the atomic theory of matter. To summarize, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of component gases. Furthermore, if we know the volume, the temperature, and the number of moles of each gas in a mixture, then we can calculate the pressure exerted by each gas individually, which is its partial pressure The pressure a gas in a mixture would exert if it were the only one present (at the same temperature and volume)., the pressure the gas would exert if it were the only one present (at the same temperature and volume). More generally, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases at a given temperature and volume is the sum of the pressures exerted by each gas alone. What is the total pressure of the mixture? Because the pressure depends on only the total number of particles of gas present, the total pressure of the mixture will simply be twice the pressure of either component. With this assumption, let’s suppose we have a mixture of two ideal gases that are present in equal amounts. Nothing in the equation depends on the nature of the gas-only the amount.
#747 MMHG TO ATM ZIP FILE#
zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.Įquation 10.24 P = n ( R T V ) = n (constant)
#747 MMHG TO ATM DOWNLOAD#
You can browse or download additional books there. More information is available on this project's attribution page.įor more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. Additionally, per the publisher's request, their name has been removed in some passages. However, the publisher has asked for the customary Creative Commons attribution to the original publisher, authors, title, and book URI to be removed. Normally, the author and publisher would be credited here. This content was accessible as of December 29, 2012, and it was downloaded then by Andy Schmitz in an effort to preserve the availability of this book.
#747 MMHG TO ATM LICENSE#
See the license for more details, but that basically means you can share this book as long as you credit the author (but see below), don't make money from it, and do make it available to everyone else under the same terms. It will be harder to breathe in the mountains because there is actually less O 2 per volume compared to at sea level.This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 license. Since gases are compressible, this creates an environment in the mountains that has less air per unit volume. In the mountains there is less air above you so less pressure. The same can be said about decreasing pressure.

The Diagram below, the pressure at point "X" increases as the weight of the air above it increases.
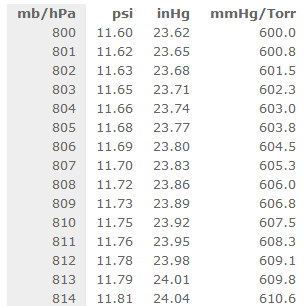
"Atmospheric Pressure" is defined as the force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weight of the air above that surface. The following is a list of all of the standard pressure in every unit for pressure.ġ Atm = 760 torr =760 mmHg = 101.325kPa = 101,325 Pa = 14.7lb/in 2 = 29.92 inHg The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa), but other pressure terms include atmospheres (atms), millimeters of mercury (mmHg), and torr. Gas pressure is a gauge of the number and force of collisions between gas particles and the walls of the container that holds them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
